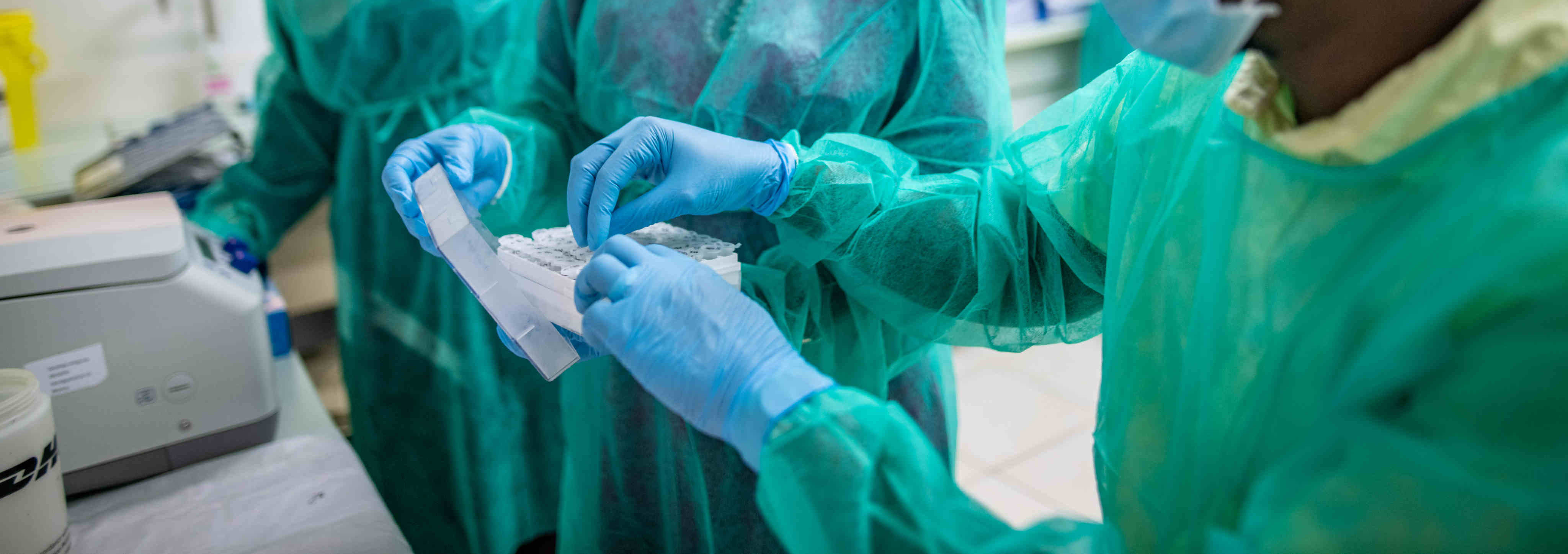
New publication by Frimpong et al. 2019 - Rapid detection of Mycobacterium ulcerans with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay
Background
Access to an accurate diagnostic test for Buruli ulcer (BU) is a research priority according to the World Health Organization. Nucleic acid amplification of insertion sequence IS2404 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the most sensitive and specific method to detect Mycobacterium ulcerans (M. ulcerans), the causative agent of BU. However, PCR is not always available in endemic communities in Africa due to its cost and technological sophistication. Isothermal DNA amplification systems such as the recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) have emerged as a molecular diagnostic tool with similar accuracy to PCR but having the advantage of amplifying a template DNA at a constant lower temperature in a shorter time. The aim of this study was to develop RPA for the detection of M. ulcerans and evaluate its use in Buruli ulcer disease.
Methodology and principal findings
A specific fragment of IS2404 of M. ulcerans was amplified within 15 minutes at a constant 42°C using RPA method. The detection limit was 45 copies of IS2404 molecular DNA standard per reaction. The assay was highly specific as all 7 strains of M. ulcerans tested were detected, and no cross reactivity was observed to other mycobacteria or clinically relevant bacteria species. The clinical performance of the M. ulcerans (Mu-RPA) assay was evaluated using DNA extracted from fine needle aspirates or swabs taken from 67 patients in whom BU was suspected and 12 patients with clinically confirmed non-BU lesions. All results were compared to a highly sensitive real-time PCR. The clinical specificity of the Mu-RPA assay was 100% (95% CI, 84–100), whiles the sensitivity was 88% (95% CI, 77–95).
Conclusion
The Mu-RPA assay represents an alternative to PCR, especially in areas with limited infrastructure.
Articles
Test Article With Image
Test article 14 July 2025 with image TL
Read moreVirtual Workshop: Recognition And Control Of Mtb Infected Cells: From Basics To The Clinic | 13 – 14June 2023
The Stop
TB Partnership Working Group on New TB Vaccines (WGNV) and the National
Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)are
co-hosting a workshop on the topic of Recognition and Control of Mtb
Infected Cells: From Basics to the Clinic. This workshop is intended to address
the need for correlates and to identify platforms that measure recognition or
control of the infected cell - especially in humans - as identified in the EDCTP/AIGHD Global Roadmap for
Research and Development of New TB Vaccines and the Strategic Framework for
New TB Vaccines in the Stop TB Partnership Global Plan to End TB 2023 - 2030.
The overall goals of this workshop
are to:
- elucidate the mechanisms by
which the immune system recognizes the Mtb-infected cell
- explore the degree to which
such recognition can lead to control of the intracellular microbe, and
- discuss the translational
implications of these observations
The workshop format will be largely
discussion-based. Each session will have three short presentations that will
provide a high-level overview of key topics within the session theme, followed
by a discussion between the session chairs, speakers, and participants.
Click here
to view the programme and
speakers.
This workshop is free of charge and
open to any participants interested in this topic.
Ssi/Isid Infectious Diseases Research Fellowships | Deadline For Applications: 16 June 2023
The International Society for Infectious Diseases (ISID) and the Swiss
Society for Infectious Diseases (SSI) are inviting applications for their joint
Infectious Diseases Research Fellowship Program. The purpose of this programme
is to support infectious disease physicians and scientists from under-resourced
countries through multidisciplinary clinical and laboratory training at a
select biomedical institution in Zurich, Switzerland. The one-year SSI/ISID
Fellowship programme is open to applicants who are 40 years or younger,
citizens and permanent residents of under-resourced countries or Eastern
Europe. The deadline for applications is 16 June 2023.
More information: https://na.eventscloud.com/eSites/748378/Homepage